The Hidden Drawbacks of HIV: Treatment Regimens may Exacerbate Risk of Knee Arthritis
A prominent class of drugs used for HIV management may accelerate osteoarthritis development
CHENGDU, SICHUAN, CHINA, July 1, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ -- Improved treatment regimens have increased the life expectancy of individuals infected with HIV. However, these individuals are at a higher risk of developing other comorbidities—one such condition that has been debated upon is osteoarthritis (OA). Now, researchers from Shanghai Jiaotong University have uncovered a link between protease inhibitors—drugs utilized in HIV management—and the acceleration of OA development.Acquired immune deficiency syndrome, or AIDS, caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), weakens the body’s immune system and can be life-threatening if left untreated. Although there is currently no cure for AIDS, the widespread use of antiretroviral therapies has successfully transformed what was once a fatal diagnosis into a manageable chronic condition. Given this increased life expectancy, the focus has now shifted to non-AIDS comorbidities such as cancer, diabetes, and even osteoarthritis (OA), since HIV-infected individuals are at a higher risk of developing these conditions than the general population. However, there has been controversy regarding the premature aging of knee joints and the prevalence of OA in HIV-infected individuals.
Now, in a study published online on June 03, 2025, in the journal Bone Research, a team of researchers led by Dr. Zanjing Zhai at Shanghai Jiaotong University in Shanghai, China, has investigated the link between protease inhibitors (PIs), a class of drugs used to manage HIV, and the potential acceleration of OA development. In addition, they explored the underlying biological mechanisms that were responsible for this association.
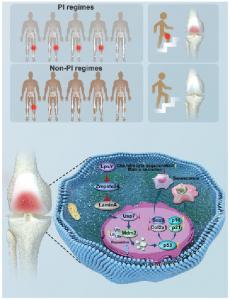
First, they studied a group of 151 HIV-infected individuals to observe if PIs (specifically, a combination of the drugs lopinavir and ritonavir) had any association with early development of OA in the knee. “Patients receiving PIs scored lower on the Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score questionnaire compared to those not receiving these medications, suggesting worse functional outcomes,” Dr. Zhai explains. Furthermore, X-ray imaging revealed a higher incidence of OA in the knees of patients treated with PIs.
The researchers then evaluated the effect of various anti-HIV drugs on chondrocytes, the specialized cells comprising cartilage—a tissue in the knee joints that undergoes deterioration in patients with OA. Experiments on cultured chondrocytes as well as mice showed that among 25 anti-HIV drugs screened, lopinavir had the most detrimental effect on chondrocytes. Lopinavir treatment accelerated chondrocyte degradation and promoted senescence, a process in which cells permanently cease growth and division, thereby contributing to the OA development.
How exactly do PIs accelerate OA development? To answer this, the researchers focused on the gene Zmpste24, which plays a role in arthritis and aging processes and has been previously reported to be inhibited by lopinavir. Interestingly, they found that lopinavir’s effects on chondrocytes were dependent on Zmpste24 expression. When the gene was ‘knocked out’ or not expressed, lopinavir no longer exacerbated chondrocyte degradation and senescence or worsened cartilage degeneration in mice.
To understand the mechanism by which lopinavir-induced inhibition of Zmpste24 accelerates OA, they explored the underlying biological pathways and genes affected in this process. They found that Zmpste24 inhibition compromises nuclear membrane stability, which disrupts the interaction between Usp7 and Mdm2 proteins. This disruption activates the p53 signaling pathway, ultimately accelerating cartilage senescence. The study also revealed increasing the expression of Zmpste24 can have the opposite effect, i.e., it can reduce the OA severity in mice.
How does this study impact the millions of people worldwide who are currently living with HIV? “This study provides new insights into PI-containing regimens and their relation to early OA development in people living with HIV and unveils a new mechanism underlying Zmpste24-related senescence,” explains Dr. Zhai. “Based on our findings, people living with HIV with elevated risk for knee OA should carefully consider their treatment options and choose other regimens when other effective alternatives are available.”
***
Reference
Titles of original papers: AIDS patients suffer higher risk of advanced knee osteoarthritis progression due to lopinavir-induced Zmpste24 inhibition
Journal: Bone Research
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-025-00431-2
Yini Bao
Editorial Office of Bone Research
+862885546461 ext.
br@scu.edu.cn
Visit us on social media:
X
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.